After the Second World War, many vehicles used by the military forces were redirected to civilian uses. Robust and versatile vehicles, which previously performed military functions, began to be used on farms, in crop fields and even for leisure. In the United States and Europe, the iconic American Jeep and the Land Rover English dominated the scene. In Germany, another utility vehicle gained relevance: the DKW Munga, produced by Auto Union, a precursor that left its legacy.
The birth of the DKW Munga

In 1954, the NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) launched a competition for the development of lightweight, robust and compact military vehicles. Among the competitors were Borgward, Porsche and DKW, which ended up winning and starting the development of the DKW F91/4 model, known as DKW SUV (off-road vehicle).
In 1962, the model was renamed Munga, an acronym for “Mehrzweck-Universal-Geländewagen mit Allradantrieb”, which means “multi-purpose universal vehicle with all-wheel drive”. It has become an essential tool for military, police and civilian use, thanks to its versatility and durability.
Munga features and versions
O DKW Munga was produced in three main versions: Munga 4, Munga 6 It is Munga 8, with capacity for four, six and eight passengers, respectively. Each version presented specific adaptations, but all shared the robust and functional essence of the model.
Munga 4
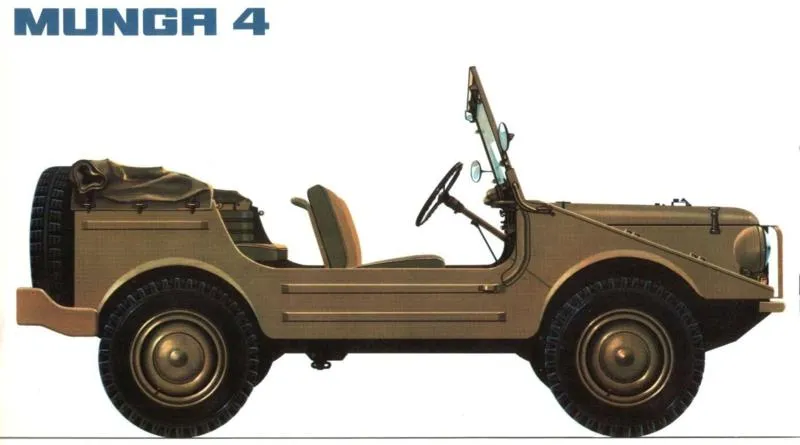

The basic version, the Munga 4, could carry four adults or accommodate a driver, passenger and a significant amount of cargo by removing the rear seats. The model measured 3.44 meters long, weighed 1,085 kg and had a load capacity of up to 690 kg. Interestingly, doors were optional, and if not installed, a chain connected the open ends to protect the passengers.
Munga 6
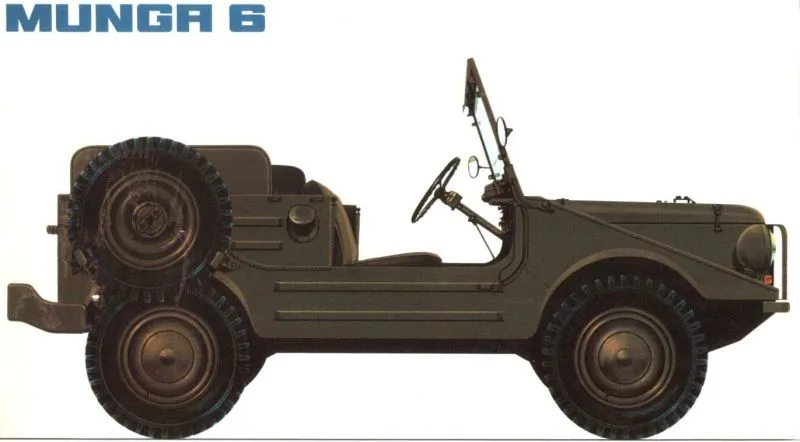

In the intermediate version, the Munga 6, there were rear seats arranged perpendicular to the front ones. The spare tire was on the right side, freeing up the small rear door for access. The length remained the same, but the total weight increased slightly, remaining around 1,100 kg.
Munga 8
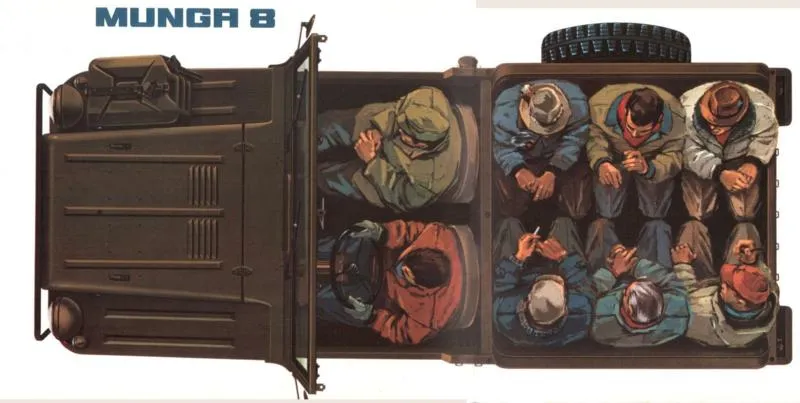

The larger version, the Munga 8, could accommodate up to eight passengers. At 3.6 meters long and weighing 1,120 kg, this configuration was more spacious, although the rear occupants traveled with their shoulders practically touching. The load capacity was adjusted to meet the needs of public transport.
Mechanics and performance
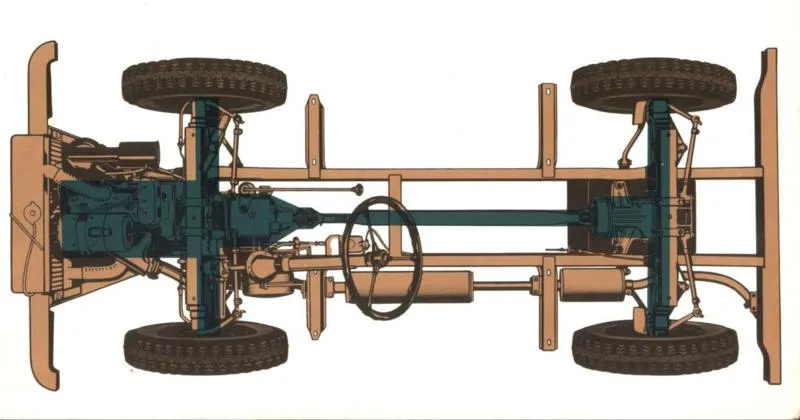
O DKW Munga was equipped with a front-mounted three-cylinder in-line engine, with 980 cm³ displacement, working in the classic system two times from DKW. This engine delivered 44 horsepower at 4,250 rpm and a maximum torque of 8 kgfm at 3,000 rpm. To work, it required a mixture of gasoline with specific oil in a ratio of 1:25.
Average consumption was approximately 9 km/l, and the maximum speed reached 98 km/h. The traction was four-wheel drive, with two differentials, and a four-speed manual gearbox, with first gear unsynchronized. The robustness of the chassis, built with parallel side members and crossbars, ensured the necessary resistance to face the most challenging terrain.
Off-road suspension and angles
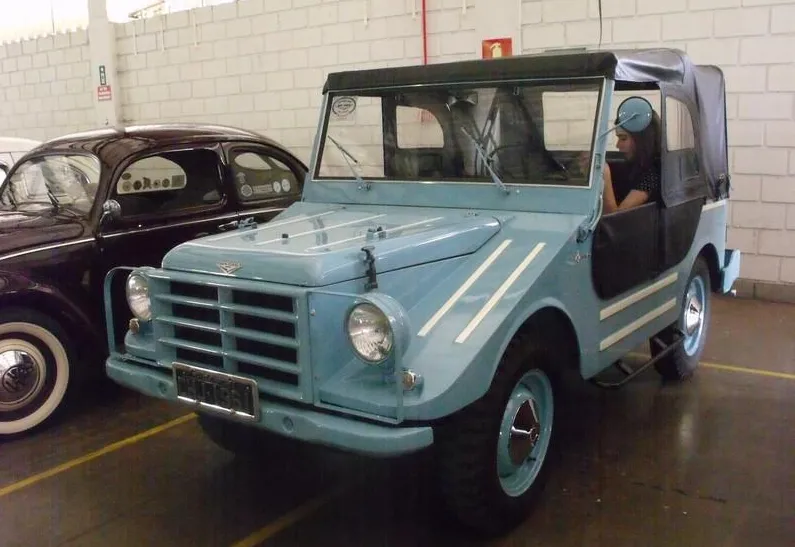

The four-wheel independent suspension, equipped with hydraulic shock absorbers, provided excellent performance on rough terrain. The entry angle of 43 degrees and the exit angle of 41 degrees (31 degrees on the Munga 8) ensured excellent ability to overcome obstacles. It was no wonder that the Munga was extremely reliable on terrain such as snow, mud and mountains.
International competitors
During the 1960s, the DKW Munga competed directly with other robust vehicles of the time, such as the Land Rover English, the Jeep CJ-5 American, the Nissan Patrol Japanese, the Toyota Land Cruiser (similar to the Bandeirante in Brazil), the Fiat Campagnola Italian and even the UAZ 469 Russian. Each had unique characteristics, but the Munga stood out for its versatility and legacy of German engineering.
Contribution to the Audi Quattro
Interestingly, Munga's all-wheel drive technology was instrumental in the development of the legendary Audi Quattro, one of the greatest rally winners in history. Audi engineers studied Munga's system and adapted it for racing cars, cementing the fame of quattro traction.
Production and legacy
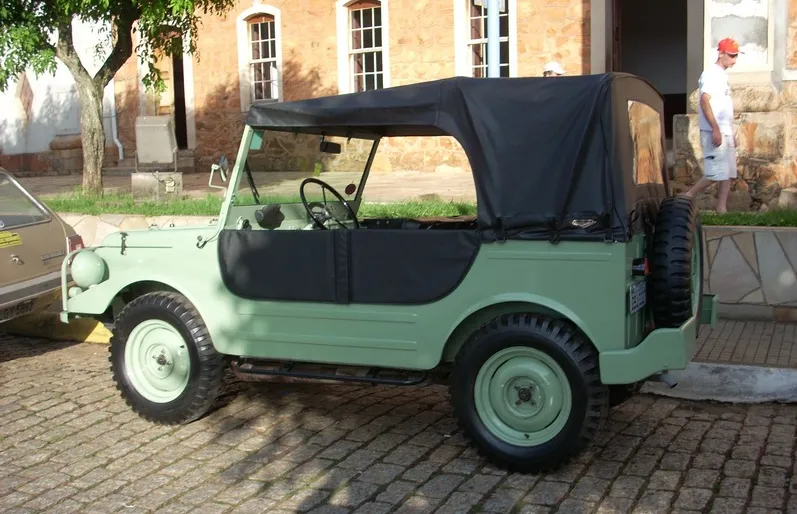

Between 1956 and 1968, approximately 75,000 units of the DKW Munga. Its importance was recognized decades later, as in 2005, when a Munga 4 model was displayed at the Audi Forum Paris, celebrating 25 years of quattro drive. Even after production ended, the Munga remains an icon among historic vehicle enthusiasts.
The DKW Candango in Brazil
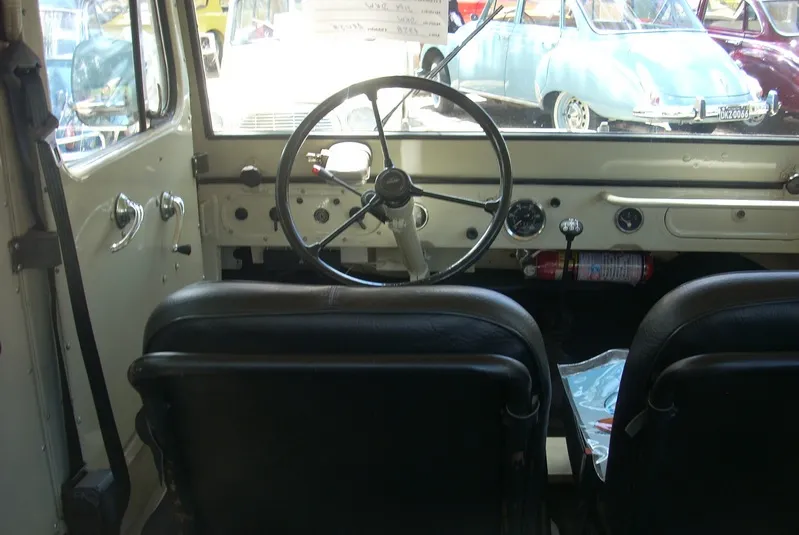

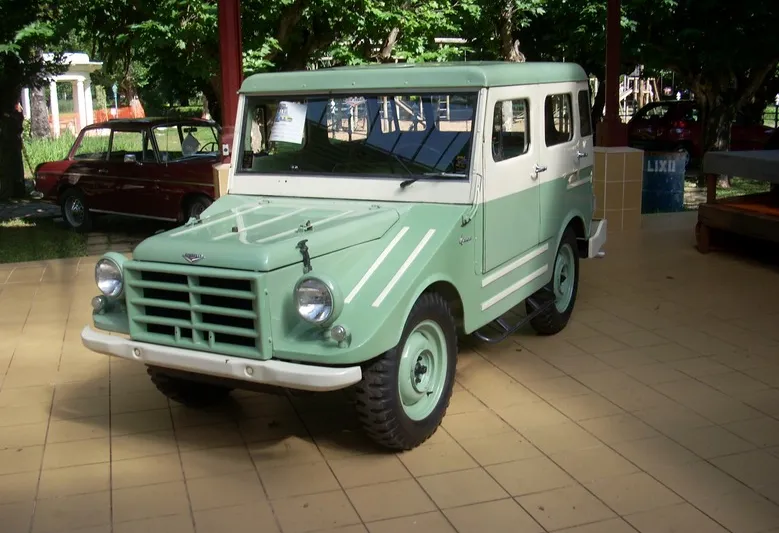
In Brazil, the DKW Munga arrived in 1958, being renamed as DKW Candango in honor of the workers who built Brasília. With an appearance similar to the Jeep Willys, the Candango was well received, but never reached mass production.
Characteristics of the national model
The Candango was manufactured by Vemag, which added some exclusive features, such as the steel hood. Initially, the model had permanent 4×4 traction, with the option of low gear engaged on the move. In 1960, it began offering versions with 4×2 traction for greater comfort in urban areas. Its two-stroke engine was easily recognized by its characteristic sound, which became a trademark.
Despite being robust, the Candango ended its production in 1963, with only 4,400 units manufactured. This was partly due to the lack of interest from the Brazilian army, which opted for other models. However, the Candango won over civilian admirers and is now a rarity appreciated at classic car shows.
Historical and cultural value
The DKW Candango holds a special place in Brazilian automotive history. It symbolizes the transition from a military vehicle to a civilian utility vehicle, adapting to the needs of a changing society. Collectors' gatherings, such as those held in Caxambu and Poços de Caldas (MG), keep the memory of this little giant alive.
Conclusion
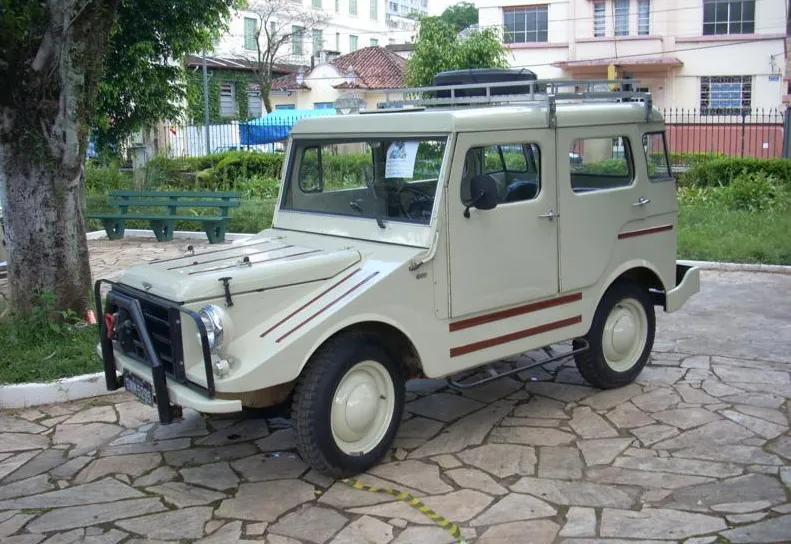

In 2025, the DKW Munga/Candango remains a symbol of versatility, strength and innovation. If you are a historic vehicle enthusiast, appreciate the rich history of this model that began as a military utility vehicle and found its place in civilian life. In Brazil, the Candango is still a rare piece and valued by collectors, with prices that can exceed R$ 150 thousand, depending on the state of conservation.
With its technological legacy influencing even icons like the Audi Quattro, the Munga/Candango continues to be proof that engineering can transcend eras, adapting to the needs of war and peace. So, if you have the opportunity to get up close to one of these models, take the opportunity to explore the roots of a history that combines innovation, functionality and resistance.









